Everything You Need to Know About Solar Inverters
Imagine harnessing the power of the sun to light up your home, charge your devices, and even run your appliances. That’s the magic of solar energy, and at the heart of this renewable energy revolution lies a crucial player: solar inverter. In this blog, we’re going to dive deep into everything you need to know about solar inverters, from their fundamental function to the latest technological advancements, you will know it all!
What is a Solar Inverter?

A solar inverter is a device that converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is suitable for powering household appliances, businesses, and the electrical grid. In simpler terms, the solar inverter is a device that makes the sun’s energy suitable for everyday electrical needs.
Features of Solar Inverters
Solar Inverters come in various types and models, each with its own set of features. However, here are some common features you might find in modern solar inverters:
1) Efficiency: Solar inverters have efficiency ratings that indicate how effectively they convert DC electricity into AC electricity. Look for inverters with high-efficiency ratings to minimize energy losses.
2) Monitoring and Data Logging: Advanced solar inverters often come with built-in monitoring systems that allow you to track the performance of your solar power system. You can monitor energy production, and system health, and even receive alerts in case of issues.
3) Remote Control: Some inverters can be remotely controlled and configured through smartphone apps or web-based interfaces, making it easier to monitor and manage your solar power system.
4) Cooling and Ventilation: Some inverters use active cooling systems, like fans, to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Proper ventilation and cooling are essential for the inverter’s longevity.
5) Load Management: Certain inverters have load management capabilities, allowing you to prioritize certain loads or appliances when there’s limited solar power availability.
6) Anti-Islanding Protection: Solar Inverters incorporate safety features such as anti-islanding protection. This prevents the inverter from sending electricity back to the grid during a power outage, protecting utility workers and the stability of the grid.
Read also: The Procedure of Net Metering for On-Grid Solar Systems
Types of Solar Inverters
There are several types of solar inverters available to suit different solar panel system configurations and requirements. Here are the most common types:
i) On-Grid Inverters:
On-grid solar inverters are specifically designed to power appliances while also allowing the surplus electricity generated to be sent to the grid. However, it’s important to note that these inverters rely on the availability of sunlight to operate effectively. In cases of power cuts, your appliances will continue to receive the necessary power, but the grid will not be able to receive any excess electricity.
ii) Off-Grid Inverters
Off-grid solar inverters come in two main types: MPPT Solar inverters and PWM Solar Inverters. These inverters are designed to power your appliances while also allowing the surplus electricity generated to be stored in the battery. What sets off-grid inverters apart is their ability to operate even in the absence of sunlight, because of the energy stored in the battery. So, during power cuts, your appliances can continue to function hassle-free, drawing power from the battery.
iii) Hybrid Inverters:
Hybrid Solar Inverters fulfill the functions of both on-grid and off-grid solar inverters. They power the appliances and efficiently store any excess electricity in the battery. Once these tasks are fulfilled, hybrid inverters redirect the remaining electricity back to the grid.
How does a Solar Inverter Work?
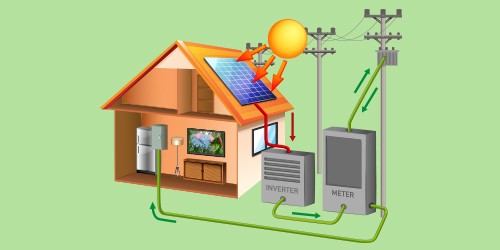
The working of the solar inverter is explained in the form of the steps given below:
i) DC Electricity Generation: Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
ii) DC to AC Conversion: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is not suitable for household appliances, which operate on AC electricity. This is where the solar inverter comes into play.
iii) Inverter Input: The DC electricity from the solar panels is fed into the solar inverter. The inverter is connected to the solar panel array, and it typically has a maximum DC input voltage and current rating that must not be exceeded.
iv) Conversion Process: Inside the solar inverter, there are electronic components, including transistors and capacitors, that perform the conversion. The main process involves switching the DC input on and off rapidly, creating a waveform that approximates a sinusoidal AC waveform.
v) Synchronization with the Grid (On-Grid Inverters): In the case of On-grid solar inverters, they power the appliances while also allowing the surplus electricity generated to be sent to the grid.
vi) AC Output: The solar inverter then produces AC electricity with the appropriate voltage, frequency, and waveform. This AC electricity is sent to the building’s main electrical panel to power appliances, lights, and other electrical loads, and the excess electricity is sent back to the grid in grid-tied systems.
Price Range of the Solar Inverter
The price of the solar inverter varies depending on the capacity of the inverter.
Hybrid Inverter- For a hybrid inverter the price starts from INR 1,00,000 for 5 kva inverter and goes up to INR 10,00,000 for a 100 kva inverter
Off-grid Inverter– For an off-grid inverter the price starts from INR 7000 for 1 kva inverter and goes up to INR 2,00,000 for a 15 kva inverter
On-grid Inverter– For an on-grid inverter the price starts from INR 50,000 for 2 kva inverter and goes up to INR 7,00,000 for 250 kva inverter.
Read also: List of Top Solar Inverter Manufacturers in India

